Did you know that Australia was the first country to pioneer the commercial use of plastic pipes in high-rise residential and commercial buildings? This groundbreaking innovation revolutionized construction practices but also brought unique fire safety challenges. Plastic pipes, while lightweight and cost-effective, are highly susceptible to melting under intense heat, leaving gaps in fire barriers that can allow fire and smoke to spread rapidly. To address this risk, fire collars were developed, and their adoption has since become a cornerstone of passive fire protection systems worldwide.
The Role of Fire Collars in Fire Safety
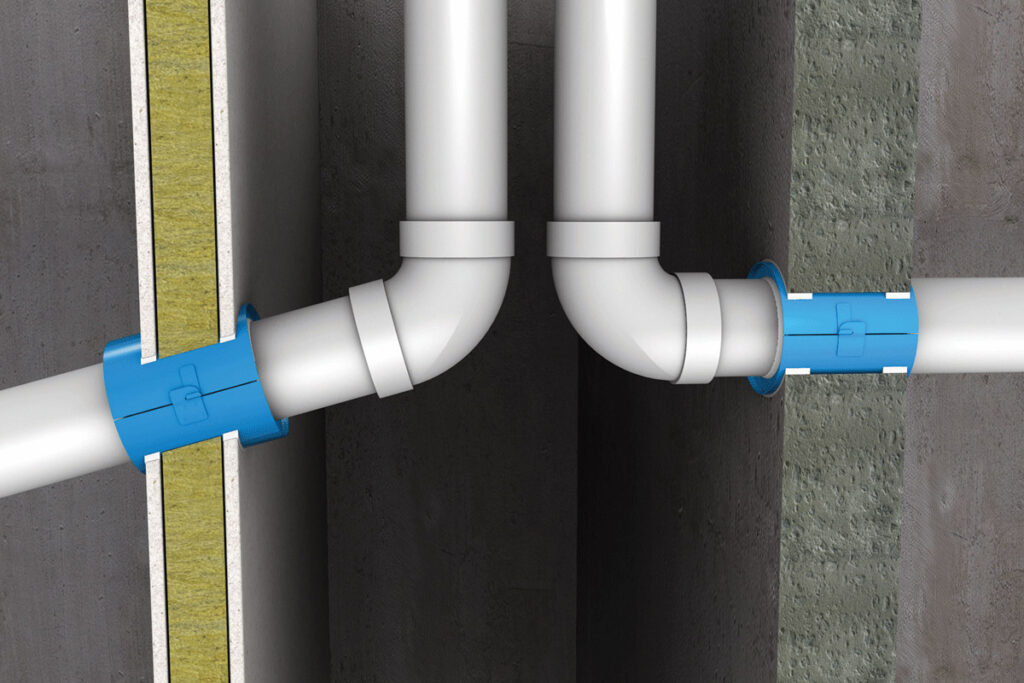
Fire collars are essential devices designed to contain the spread of fire and smoke through pipe penetrations in walls and floors. These devices incorporate intumescent materials—substances that expand when exposed to heat. During a fire, the intumescent material within the collar swells to seal the opening left by softened or melted plastic pipes. This critical function ensures the integrity of fire barriers, slowing the spread of fire and allowing occupants more time to evacuate while reducing structural damage.
From Sodium Silicate to Advanced Graphite-Based Materials
Over the years, fire collars have undergone significant evolution. Early fire collars relied on sodium silicate-based intumescent materials. While effective at the time, these materials had limitations, including slower activation in fires and vulnerability to moisture and environmental factors.
Modern fire collars, however, have embraced advanced graphite-based intumescent materials. These materials offer several advantages:
- Faster Activation: Graphite-based intumescent respond more quickly to heat, providing a more immediate seal during a fire.
- Environmental Resilience: They are resistant to water, humidity, and other environmental factors, ensuring long-term reliability.
- Durability: Modern fire collars often match the lifespan of the buildings they protect, making them a cost-effective and sustainable choice for fire safety.
Additionally, some fire collars now incorporate silicone and acrylic sealants as alternative intumescent materials, broadening the range of applications in passive fire protection.

Versatile Designs for Modern Construction Needs
Fire collars are available in a variety of designs to accommodate diverse building needs. In new construction projects, collars are typically integrated during the installation of pipe systems, ensuring seamless compliance with fire safety regulations. Retrofitting projects, on the other hand, require specialized collars designed to be installed around existing pipes. This flexibility ensures that older buildings, where passive fire protection may have been inadequate or overlooked, can be brought up to modern safety standards.
The Influence of Regulations and Technology
Fire safety regulations and building codes play a crucial role in shaping the demand for fire collars. In residential, commercial, and industrial buildings, where the risk of fire spreading through pipe penetrations is significant, compliance with these regulations is mandatory. As a result, the global adoption of fire collars continues to grow.
Technological advancements have further propelled the development of fire collars. Manufacturers are continually innovating to create more efficient designs and materials. These advancements ensure that fire collars remain effective even under extreme conditions, providing peace of mind to builders, occupants, and regulators alike.
A Crucial Component of Passive Fire Protection
The integration of fire collars into modern construction highlights their importance in passive fire protection strategies. By preventing the spread of fire and smoke through pipe penetrations, fire collars contribute to the overall safety and resilience of buildings. With ongoing advancements in materials and design, fire collars are set to remain a vital element in fire safety for decades to come.
From their origins in Australia to their global adoption, fire collars exemplify how innovation can address evolving challenges in construction and safety. Today, they stand as a testament to the importance of combining technology, regulation, and design to protect lives and property.